By Jim Ellis
Aug. 31, 2021 — Losing a congressional seat is nothing new to the Michigan delegation. Since the 1980 census, inclusive, the state has lost a district in every reapportionment and two in the 1990 iteration. Today, we continue our series about the states gaining and losing congressional districts under 2020 national reapportionment with a look at the Wolverine State.
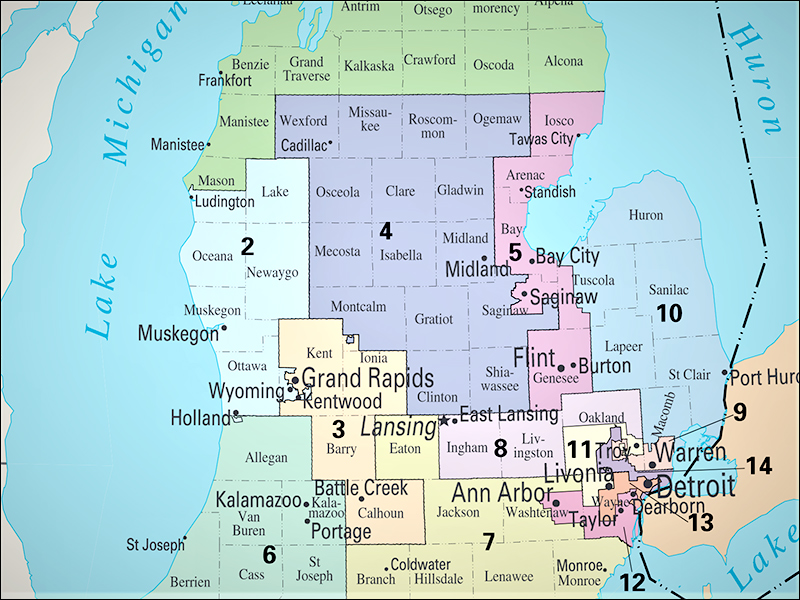
Michigan is difficult to draw not only because of the consistent seat losses, but so many of the state’s districts abut immovable objects: i.e., an international or state border, or a body of water. Under the current map, 10 of Michigan’s 14 congressional districts at least partially border a country, state, or lake.
The Michigan per district population number for the 2020 census is a high 775,179 individuals. High per district resident numbers often occur when a state loses a seat. In this case, all of Michigan’s 14 districts must gain population, hence the underlying reason for another delegation reduction.
Another factor in making the state a rather unique draw for the new Michigan Independent Citizens Redistricting Commission that is tasked with creating the new congressional map for the initial time, is the areas needing to gain the most population lie in opposite ends of the state. This, added to the fact that over 70 percent of the current districts border an immovable object, means the 2021 redistricting process is a significant challenge for the eleven commissioners (4R; 3D; 4N) with no previous experience in drawing political maps.
The area with the largest population shortfall comes in the northern part of the state. Rep. Dale Kildee’s (D-Flushing/Flint) 5th District is the seat furthest away from the population quota, down 104,476 individuals. Directly to his west, Rep. John Moolenaar’s (R-Midland) 4th District is 77,325 people under quota, and to the north all the way to the Canadian border, Rep. Jack Bergman’s (R-Watersmeet) Upper Peninsula 1st District will require an additional 70,829 residents. Combined, these three seats are 252,630 people short of the population quota for three congressional districts.
The area in the second-most need of population is the city of Detroit. The two districts that encompass the city, Districts 13 (Rep. Rashida Tlaib-D) and 14 (Rep. Brenda Lawrence-D) are a combined 184,290 people short for a pair of districts. Because both CDs 13 and 14 and majority minority seats, it is more than probable that the commission won’t collapse these districts because of Voting Rights Act requirements.




 By Jim Ellis
By Jim Ellis