By Jim Ellis — Tuesday, Dec. 16, 2025
Redistricting
The redistricting wars may be coming to a head. Recent action has occurred in several states providing a better national redistricting picture in preparation for the 2026 election.Below is a synopsis of the latest developments:
California: After a majority of California voters approved the special election redistricting referendum, a racial gerrymandering lawsuit was filed against the state’s new map.
Meanwhile, the US Supreme Court issued a stay on the Texas racial gerrymandering lawsuit, with a rebuke from Justice Samuel Alito to the three-judge panel in El Paso for rendering a decision before the high court ruled on a related Louisiana racial gerrymandering case. Thus, it became clear that all other cases would be held until the high court issues what could be a landmark ruling.
The judicial action likely means the new California map will be in place for the 2026 election. The original map proponents believe the plan will return five more seats for the Democrats, reducing the Republicans to just four of 52 Golden State districts.
Florida: Late last week, Gov. Ron DeSantis (R) said that the state will redistrict the congressional map and do so during the Spring. The Florida primary is not scheduled until Aug. 18, so time remains to complete the redistricting process. It is possible that Republicans could gain two seats from a new map.
Georgia: A new Georgia map has been completed. The legislature made minor changes to the existing plan that will not likely affect the current partisan division (9R-5D).
Indiana: Late last week, the Indiana state Senate defeated a redistricting map that the state House passed. The plan would have converted two Democratic seats to Republican, thus sweeping the nine-member delegation. Unless the Senate reconsiders the action, the current 7R-2D map will remain intact for the 2026 election.
Louisiana: The US Supreme Court is considering the Callais racial gerrymandering case that could become the vehicle for the justices to render a landmark racial gerrymandering decision. A ruling was expected in June, but the justices postponed their opinion and ordered a second round of oral arguments. The subsequent hearing was held Oct. 15, and all await a final determination.
If the court upholds the lower court decision, the current Louisiana map will be invalidated, meaning the Republicans will likely gain one seat. Should this be the Supreme Court’s ultimate decision, then the possibility exists that the Alabama map will also be redrawn because its plan is virtually identical to Louisiana’s.
Maryland: In a situation similar to what is found in Indiana, most of the Maryland Democratic political establishment favors attempting to collapse their one Republican congressional district, but the state Senate leadership refuses to take action. Therefore, unless the Senate President completely reverses himself, a new redistricting map will not be enacted.
Missouri: The Missouri legislature and Governor have enacted a new map that will likely convert the Kansas City anchored 5th CD from Democratic to Republican. Opponents of the map, officially organized under a group name entitled People Not Politicians, have collected double the number of signatures needed to force a special election initiative vote with the goal of repealing the new map. If a ruling is made qualifying the initiative for the ballot, voters will then decide if the new map will stand.
Under Missouri procedure, simply qualifying the initiative will suspend the new map. This means the state would be forced to revert to the 2021 map for the 2026 election. An initiative vote would occur in the regular election cycle. If the voters adopt the new plan, it would take effect in the 2028 election cycle.
North Carolina: The legislature’s new congressional map will almost assuredly stand for the 2026 election. The initial complaint protesting the plan was rejected at the lower court level. The US Supreme Court’s action involving the Texas case suggests that no further judicial movement will occur on the new North Carolina plan before the candidate filing deadline on Dec. 19. Therefore, it is likely that Republicans will gain one seat in the Tar Heel delegation.
Ohio: The bipartisan elected official redistricting commission unanimously agreed upon a new congressional map, one that state law mandated be drawn. Under the Ohio procedure, a unanimous decision from the redistricting panel, which included Gov. Mike DeWine (R), means the map is officially enacted without action from the state legislature. The new plan will likely produce a one seat gain for Republicans in western Ohio, with the outside possibility of a second conversion in Cincinnati.
Texas: As discussed above, the Supreme Court stayed the three-judge panel decision that ruled the new map a racial gerrymander. Candidate filing has concluded, so the new 2025 map will be in place for the 2026 elections. The original map proponents believe the plan will return five more seats for the Republicans.
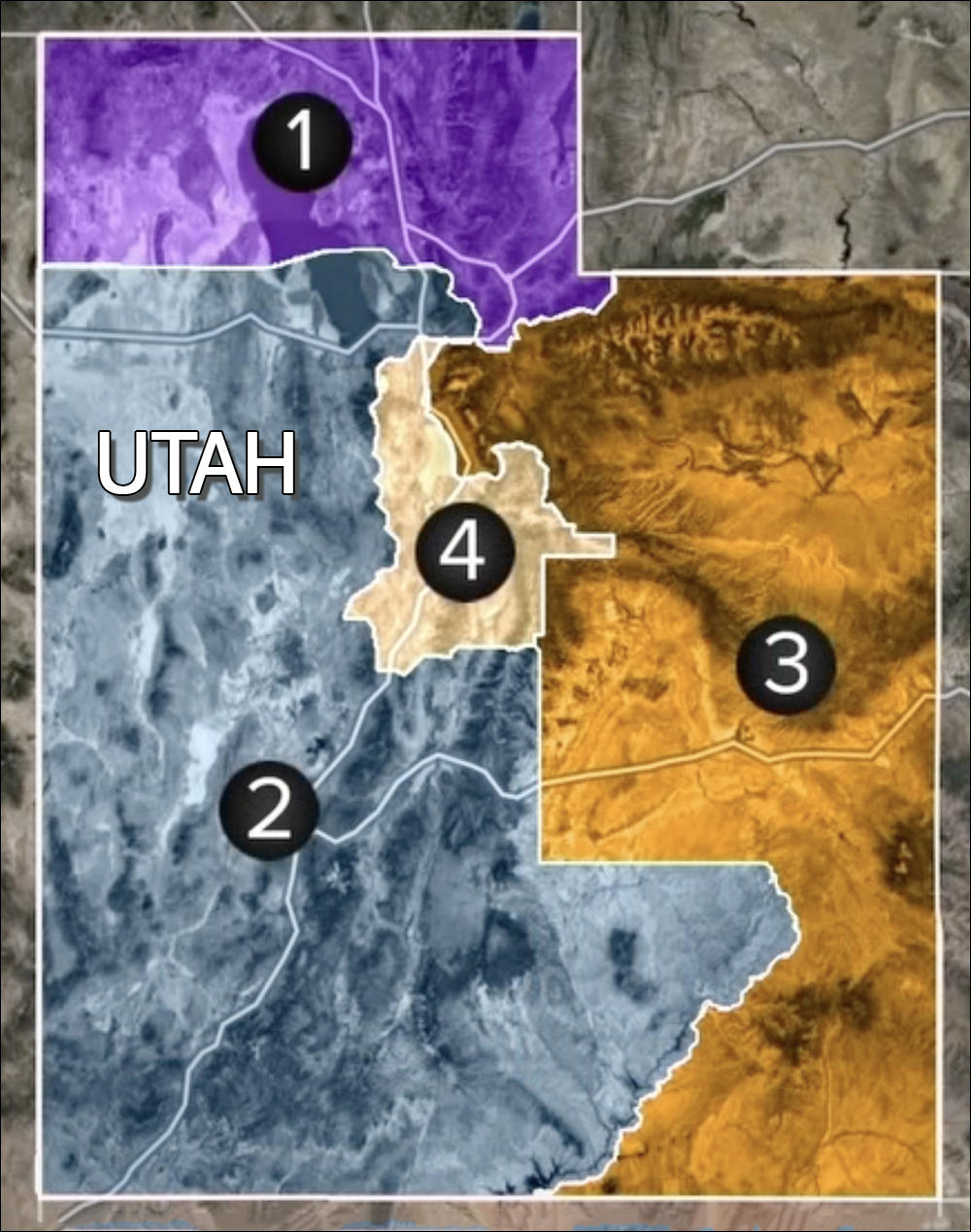
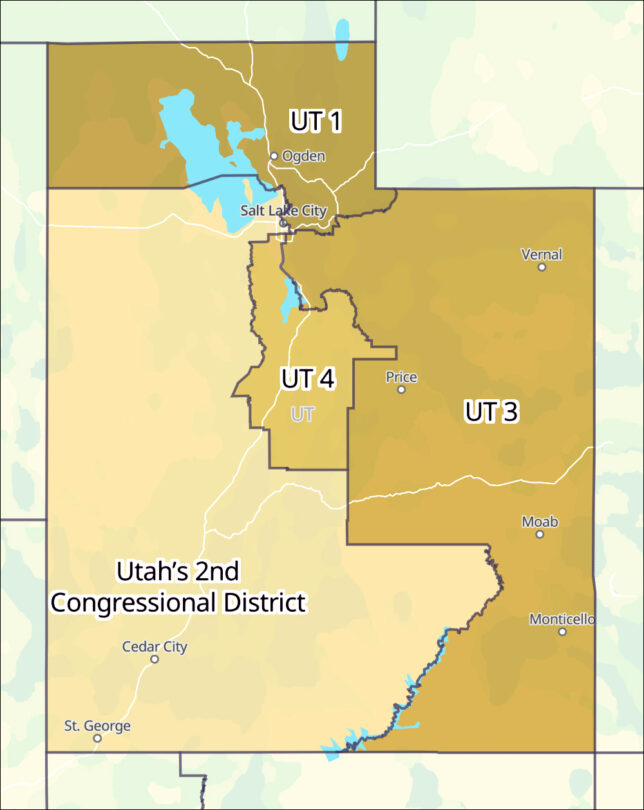
Utah: A state court ruled that the legislature ignored certain criteria that voters adopted in a previous redistricting initiative. Therefore, the 2021 map was declared invalid, a ruling that the state Supreme Court sustained. The court then adopted a new map that created a Salt Lake City Democratic seat. The new plan will produce a 3R-1D map for the 2026 election, which is a gain of one Democratic seat.
Virginia: The Old Dominion redistricting effort may determine which party wins the national redistricting wars. With the Democrats gaining full control of the state government, the new legislature must pass a referendum for the ballot when they convene in January. The measure will have to fulfill other legal requirements, and a special statewide referendum election is required. Voters would have to approve a new map before the April 2 candidate filing deadline for the June 16 primary election.
Democrats claim they can draw a map that will relegate Republicans to just one seat in the 11-member delegation. Currently, the Virginia congressional districts split 6D-5R. A four-seat swing in this state could tip the balance of power toward the Democrats in their quest for the US House majority.