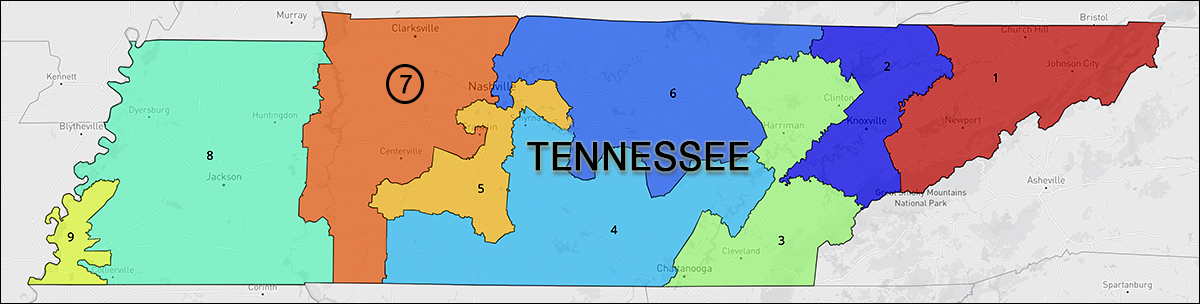
Tennessee Congressional Districts (Click on map to see interactive version at: Dave’s Redistricting App.)
By Jim Ellis — Friday, Nov. 21, 2025
US House
The Dec. 2 special election to fill the Tennessee open congressional seat should be a slam dunk for the Republicans, but new polling data and outside money coming into the district for both sides infer this contest will be closer than expected.
We’ve seen two recent polls, both producing similar ballot test results. The first is from Workbench Strategies for Democratic nominee, state Rep. Aftyn Behn’s campaign (Oct. 15-19; 400 likely TN-7 special election voters), that found Republican former state cabinet secretary Matt Van Epps leading by a 51-41 percent clip.
The second poll, from Impact Research and taken within the same time frame (Oct. 16-19; 700 likely TN-7 special election voters), produced a similar 52-44 percent result in Van Epps’ favor. The polls suggest the race could become closer as the margin between the two candidates are at least slightly under where the Republican nominee should stand at this point in the campaign.
The Volunteer State’s 7th District was changed dramatically in the 2021 redistricting plan. In order to convert the Nashville-anchored 5th District to the Republicans, the 7th CD had to give up GOP territory. Therefore, what was typically a high 60s Republican seat became a high 50s district.
The 7th District from the previous decade carried a partisan lean of 66.1R – 31.6D (Dave’s Redistricting App calculations) when then-Reps. Marsha Blackburn (R) and Mark Green (R) successively held the seat. Blackburn, of course, is now in the Senate and running for Governor. Green resigned from Congress earlier in the year to pursue an opportunity in the private sector, thereby opening the current 7th District for the special election.
The 2021 TN-7 version for the current decade posts a much different partisan lean, again according to the Dave’s Redistricting App statisticians. The current numbers yield a 55.1R – 42.2D, or a net Democratic net gain of 21.6 percentage points. This means instead of a Republican candidate finishing near 70 percent, the new numbers would suggest victories in the mid to high 50s.
While the statistics show that a typical Republican candidate should still win easily under the new 7th District boundaries, and so far, they have (President Trump ’24: 60-38%; Rep. Green ’24: 59-38 percent), anything can happen in a low turnout special election. Democrats are riding high with momentum coming from the November 4th elections in New Jersey, Virginia, and New York City, and they believe the trend will continue in Tennessee.
The Virginia turnout numbers are telling and could give us an insight into what might happen in Tennessee. The final Virginia numbers actually showed a two percent drop-off in turnout when compared to 2021. The conclusion was Republican election day turnout proved poor, thus leading to the landslide Democratic victory.
The situation again dictates that the Tennessee Republicans will have to find a better way of convincing what is termed “the casual Trump voter” — that is, the person who will vote when President Trump is on the ballot but typically is not a regular voter — to participate in the special election.
While only spending $188,000 to win the special primary in a four-way Democratic field that featured two other state Representatives, Behn eked out a close victory with just 27.9 percent of the vote. The fourth-place finisher garnered 23.1 percent to illustrate how evenly distributed the votes were among contenders.
The situation is different for the special general. Though financial reports past Sept. 30 are not yet available, it is clear that Rep. Behn will have adequate resources to compete.
She can also count on support from left-of-center national organizations coming into the district to independently help her effort, but such is now being countered to a significant degree from at least two organizations on the right, the Club for Growth and an organization entitled Conservatives for American Excellence.
The stakes are now high for this special election in a Republican district. It is one thing for Republicans to lose big in three anti-Trump domains such as New Jersey, Virginia, and New York City. It is quite another if the Democratic nominee prevails in a special election from a strong Republican seat. With early voting now underway, the closing weeks for this campaign will prove quite interesting.