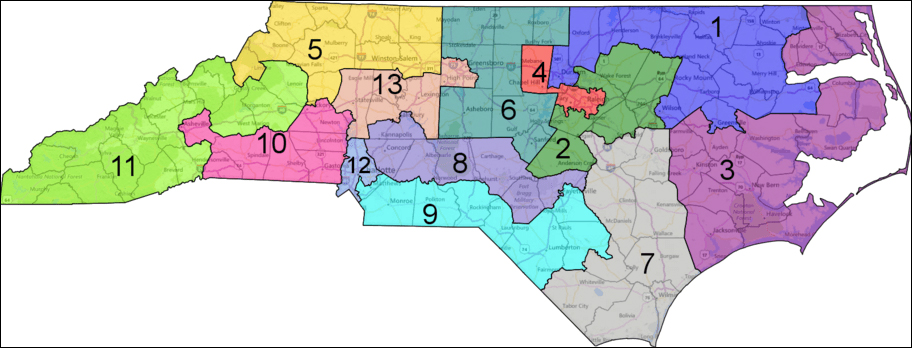
The Ohio State Supreme Court invalidated the state’s newly enacted congressional map and returned the plan to the Ohio state legislature to be redrawn. The state lost a seat in reapportionment. (Map: Dave’s Redistricting App)
By Jim Ellis
Jan. 19, 2022 — The Ohio State Supreme Court, on a 4-3 vote with the Republican Chief Justice Maureen O’Connor voting with the three Democratic members, last Friday invalidated the state’s newly enacted congressional map and returned the plan to be redrawn. The decision may result in a blow to Republican hopes of re-capturing the US House majority as the Ohio draw is one of the party’s most important maps.
The high court’s action followed a similar 4-3 decision the previous day to reject the state House and Senate maps. All of the plans were invalidated for the same reason: they did not meet the competitiveness provision in the Ohio redistricting proposition that the people’s vote enacted prior to the commencement of the re-mapping process. The justices claimed the plan must better reflect the partisan statewide voting pattern, a measure that favors Republicans but not to the extent of the district ratios projected for the jettisoned maps.
The current Ohio congressional map stands at 12 Republicans and four Democrats. The state lost a seat in reapportionment, so the advisory redistricting commission members and the legislature were tasked with creating a new 15-district congressional plan.
By most accounts, the new map would have likely elected 10 Republicans and two Democrats, while featuring three politically marginal districts, those of Reps. Steve Chabot (R-Cincinnati) and Marcy Kaptur (D-Toledo) and an open seat largely created because Reps. Anthony Gonzalez (R-Rocky River) and Tim Ryan (D-Warren) are leaving their seats to retire and run for the Senate, respectively. Therefore, the state’s electoral split could have swung anywhere from 10R-5D all the way to 13R-2D.
The ruling likely creates the greatest change for two of the aforementioned members. The court specifically cited the Hamilton County draw in Rep. Chabot’s seat that attached a swath into downtown Cincinnati. This created a city attachment to Butler County, thus placing it in Rep. Warren Davidson’s (R-Troy) strongly Republican 8th District. As a result, the 1st District became more Republican for Chabot, but still left him with a swing seat at best.




 Nov. 20, 2019 — If it seems like the North Carolina redistricting process has dragged on for the entire decade, then your senses are correct, because it has. After seeing a mid-decade re-draw before the 2016 elections, another set of lines will be in place for 2020, and then another plan for the ensuing electoral decade beginning in 2022 will be enacted during the regular decennial process. North Carolina is a sure bet to gain a new congressional seat in 2020 reapportionment.
Nov. 20, 2019 — If it seems like the North Carolina redistricting process has dragged on for the entire decade, then your senses are correct, because it has. After seeing a mid-decade re-draw before the 2016 elections, another set of lines will be in place for 2020, and then another plan for the ensuing electoral decade beginning in 2022 will be enacted during the regular decennial process. North Carolina is a sure bet to gain a new congressional seat in 2020 reapportionment.