By Jim Ellis — Monday, June 12, 2023
President
State Polls: Republican Race Getting Tighter — Two very recent Republican presidential state polls were released late last week, one from Wisconsin and the other in Utah. While the Wisconsin spread is typical of what we are seeing in other places, the Utah poll has closed to within one percentage point.Public Policy Polling (June 5-6; 507 likely Wisconsin voters) sees former President Donald Trump leading the Wisconsin GOP primary but with well less than majority support. The ballot test gives the former president a 41-25 percent lead over Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis. Ex-Vice President Mike Pence is next with eight percent support, and no one else breaks five percent. In an isolation question featuring Trump and DeSantis, the former pPresident leads this only 43-39 percent.
The Utah numbers are much closer. In this Dan Jones & Associates poll for the Utah Republican Party (May 22-June 1; 421 registered Utah Republican voters), Trump’s advantage is only 27-26 percent over Gov. DeSantis.
Former Rep. Liz Cheney, not even a candidate, places third with seven percent, and no other candidate breaks the five percent mark. However, this poll’s long sampling period and small respondent universe, along with the introduction of Cheney into the mix, casts an accuracy shadow over this poll.
Senate
Wisconsin: Polling Leader Emerges; Not the GOP’s Top Choice — The Wisconsin Public Policy Polling survey (see President section above) also tested the state’s US Senate race featuring two-term incumbent Tammy Baldwin (D).
The Republican primary ballot test suggests that former Milwaukee County Sheriff David Clarke would lead a prospective group of GOP candidates with 40 percent preference. Placing second is Rep. Mike Gallagher (R-Green Bay) with 20 percent, followed by Rep. Tom Tiffany (R-Minocqua) at 10 percent. Clarke is not an official candidate, and viewed as someone who would be unlikely to win the general election. So far, Rep. Gallagher has not made a discernible move to enter the Senate race. Rep. Tiffany is testing the waters.
The Wisconsin race could become competitive, but Sen. Baldwin would begin any general election as the favorite to win in November.
House
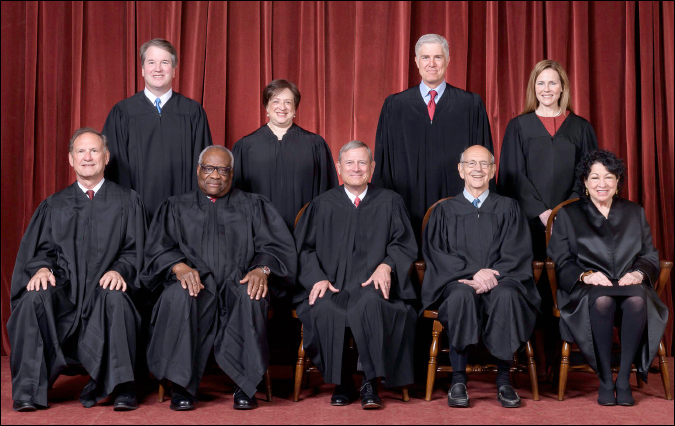
Redistricting: SCOTUS Rules on Alabama — The US Supreme Court, on a 5-4 decision with Chief Justice John Roberts and Associate Justice Brett Kavanaugh joining the majority, ruled in favor of the plaintiffs in the Alabama racial gerrymandering case. Therefore, the Alabama map will be redrawn to reflect a second minority district from the state’s seven seats. Louisiana will likely have to be redrawn as well.
Possible redraws could occur in several other southern states. The ruling is clearly a win for the Democrats and gives them even better odds of re-capturing the House majority in the 2024 election.
UT-2: Special Election Set — Since Utah Rep. Chris Stewart (R-Farmington) submitted an irrevocable letter of resignation for Sept. 15 to Gov. Spencer Cox (R), that action has allowed the state’s chief executive to set at least the special primary election even before the congressman officially leaves office.
Under Utah law, the governor must schedule the special congressional election concurrent with another election. The municipal elections were scheduled for Aug. 15 and Nov. 7, but Gov. Cox is preparing to send the legislature a measure to change those dates to Sept. 5 and Nov. 21 and add the special congressional election to that ballot. These dates meet the federal electoral notice requirements.
The legislature is expected to comply. If they do not, the 2nd District seat could remain vacant for more than a year awaiting the regular primary schedule.
In this instance, the seat will be filled while Rep. Stewart remains in office, which is similar to the Oklahoma law that allows a resigning elected official to serve until a replacement is selected.